Directed flow from color glass condensate R.J. Fries and G. Chen The initial state of nuclear collisions at very high energies

Color Glass Condensate in High Energy QCD Kazunori Itakura SPhT, CEA/Saclay 32 nd ICHEP at Beijing China 16 Aug ppt download

PPT – Theoretical Aspects of the Color Glass Condensate and Glasma PowerPoint presentation | free to view - id: 1cf974-ZDc1Z

The dipole scattering amplitude in the color glass condensate framework... | Download Scientific Diagram

Left: illustration of flow event plane de-correlations as a function of... | Download Scientific Diagram
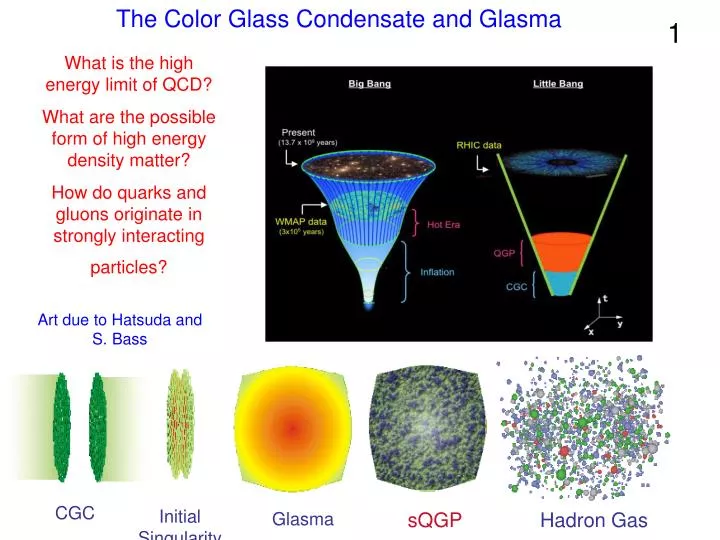
![PDF] Color glass condensate and its relation to HERA physics | Semantic Scholar PDF] Color glass condensate and its relation to HERA physics | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/d29d04dd02df53635c096084fbe670ff3299eae6/2-Figure1-1.png)